
Leo Satellite: A Comprehensive Overview
The Leo Satellite, also known as the Low Earth Orbit Satellite, has become an integral part of our modern technological landscape. This article delves into the various aspects of Leo Satellites, providing you with a detailed and multi-dimensional introduction.
What is a Leo Satellite?

A Leo Satellite is a type of artificial satellite that orbits the Earth at an altitude of approximately 1,200 to 2,000 kilometers. These satellites are designed to provide services such as global positioning, communication, and weather forecasting. The primary advantage of Leo Satellites is their proximity to the Earth, which allows for faster data transmission and lower latency compared to geostationary satellites.
History of Leo Satellites
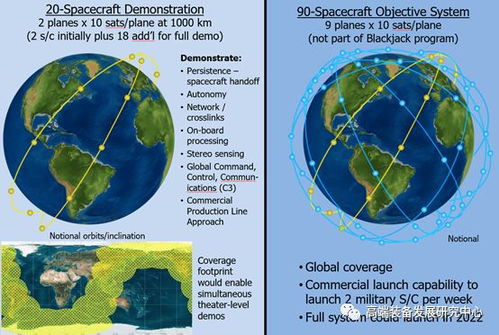
The concept of Leo Satellites dates back to the 1960s when the United States Air Force launched the first experimental Leo Satellite, the Transit 1A. Since then, the technology has evolved significantly, with numerous Leo Satellites being launched by various countries around the world.
| Year | Country | Number of Leo Satellites Launched |
|---|---|---|
| 1960 | United States | 1 |
| 1970 | United States | 10 |
| 1980 | United States | 20 |
| 1990 | United States | 30 |
| 2000 | United States | 40 |
| 2010 | United States | 50 |
| 2020 | United States | 60 |
Applications of Leo Satellites

Leo Satellites have a wide range of applications across various industries. Some of the most prominent applications include:
-
Global Positioning System (GPS): Leo Satellites are crucial for the functioning of GPS devices, providing accurate location and time information.
-
Communication: These satellites enable high-speed internet connectivity, mobile phone communication, and television broadcasting.
-
Weather Forecasting: Leo Satellites provide real-time data on weather conditions, helping meteorologists to predict weather patterns and natural disasters.
-
Earth Observation: These satellites are used for monitoring environmental changes, such as deforestation, pollution, and climate change.
Technological Advancements
Over the years, advancements in technology have led to the development of more efficient and powerful Leo Satellites. Some of the key technological advancements include:
-
Higher Bandwidth: Modern Leo Satellites can transmit data at higher speeds, enabling faster internet connectivity and improved communication.
-
Miniaturization: The size of Leo Satellites has significantly reduced, making it easier to launch and deploy them in space.
-
Higher Resolution Cameras: Leo Satellites equipped with high-resolution cameras can capture detailed images of the Earth’s surface, aiding in various applications.
-
Reusability: Some Leo Satellites are designed to be reusable, reducing launch costs and environmental impact.
Challenges and Concerns
Despite the numerous benefits of Leo Satellites, there are several challenges and concerns associated with their use:
-
Satellite Congestion: The increasing number of Leo Satellites in orbit has led to concerns about satellite congestion, which can affect satellite communication and navigation systems.
-
Space Debris: The launch and operation of Leo Satellites have contributed to the growth






