
Have you ever wondered about the fascinating world of Low Earth Orbit (LEO) satellites? These celestial wonders play a crucial role in modern communication, navigation, and scientific research. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of LEO orbits, exploring their characteristics, applications, and the technology behind them.
What is a Low Earth Orbit (LEO)?

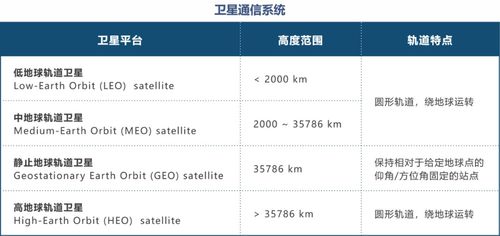
LEO is a geostationary orbit that is relatively close to the Earth’s surface, typically ranging from 160 to 2,000 kilometers above it. This proximity allows LEO satellites to complete an orbit around the Earth in approximately 90 minutes, making them ideal for various applications.
Characteristics of LEO Orbits
Here are some key characteristics of LEO orbits:
| Orbital Altitude | Range | Orbital Period | Orbital Inclination |
|---|---|---|---|
| 160 to 2,000 kilometers | Relatively close to the Earth’s surface | Approximately 90 minutes | 0 to 50 degrees |
LEO satellites have several advantages over other types of orbits, such as:
- Lower latency: The shorter distance between the satellite and the Earth results in lower communication delays.
- Higher bandwidth: LEO satellites can provide higher data rates due to their closer proximity to the Earth.
- Reduced power consumption: The lower altitude of LEO satellites requires less power to maintain their orbit.
Applications of LEO Satellites

LEO satellites have a wide range of applications, including:
- Communication: LEO satellites are used for mobile communication, internet connectivity, and broadcasting.
- Navigation: They provide accurate positioning data for GPS and other navigation systems.
- Earth Observation: LEO satellites are used for monitoring the Earth’s environment, climate, and natural resources.
- Scientific Research: They enable researchers to study the Earth’s atmosphere, space weather, and other phenomena.
LEO Satellite Constellations
LEO satellite constellations are groups of satellites that work together to provide comprehensive coverage. Some of the most notable LEO satellite constellations include:
- Starlink: A project by SpaceX to provide global internet connectivity using thousands of LEO satellites.
- OneWeb: A satellite internet company that aims to provide internet access to underserved regions of the world.
- Iridium: A satellite communication company that provides voice, data, and internet services using a network of LEO satellites.
Technology Behind LEO Satellites
LEO satellites rely on several key technologies to function effectively:
- Telemetry, Tracking, and Command (TT&C): This technology allows ground stations to monitor and control the satellite’s operations.
- Antennas: Satellites are equipped with various types of antennas to communicate with ground stations and other satellites.
- Power Systems: LEO satellites require efficient power systems to generate and manage the energy needed to operate.
- Onboard Computers: These computers manage the satellite’s operations and process data received from sensors and other sources.
Challenges and Future of LEO Satellites
While LEO satellites offer numerous benefits, they also face several challenges:
- Space Debris: The rapid deployment of LEO satellite constellations has raised concerns about space debris and its potential impact on other satellites and space missions.
- Interference: The increasing number of LEO satellites may lead to interference with other satellite systems and ground-based communication networks.
- Orbit Debris: The accumulation of space debris in LEO orbits poses a risk to the health and longevity of LEO satellites.





