
Leo Orbit Altitude: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding the altitude of the Leo orbit is crucial for anyone interested in space exploration and satellite technology. The Leo orbit, also known as the geostationary equatorial orbit, is a highly sought-after position for communication satellites. In this article, we delve into the various aspects of the Leo orbit altitude, providing you with a detailed and multi-dimensional perspective.
What is the Leo Orbit?

The Leo orbit is a geostationary orbit located at an altitude of approximately 35,786 kilometers (22,236 miles) above the Earth’s equator. This orbit is named after the constellation Leo, as it lies in the same direction as the Earth’s rotation. Satellites in this orbit appear to be stationary from the ground, making them ideal for applications such as television broadcasting, weather forecasting, and telecommunications.
Why is the Leo Orbit Altitude Important?
The Leo orbit altitude is significant for several reasons. Firstly, it allows satellites to maintain a constant position relative to the Earth’s surface, which is crucial for applications that require continuous coverage. Secondly, the altitude ensures that the satellite’s signal travels at the same speed as the Earth’s rotation, minimizing signal delay and ensuring a stable connection. Lastly, the Leo orbit altitude provides a clear line of sight between the satellite and the ground, reducing interference and signal loss.
Technical Details of the Leo Orbit Altitude

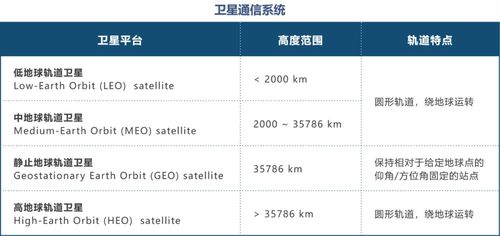
The Leo orbit altitude is determined by the balance between the Earth’s gravity and the centripetal force required to maintain the satellite’s orbit. This balance is achieved at an altitude of approximately 35,786 kilometers. At this altitude, the satellite’s orbital period matches the Earth’s rotational period, resulting in a stationary position relative to the Earth’s surface. The following table provides a comparison of the Leo orbit altitude with other orbits:
| Orbit Type | Altitude (km) | Orbital Period (hours) |
|---|---|---|
| Leo Orbit | 35,786 | 24 |
| Low Earth Orbit (LEO) | 160-2,000 | 90-120 |
| Middle Earth Orbit (MEO) | 2,000-35,786 | 4-12 |
| High Earth Orbit (HEO) | 35,786-200,000 | 12-24 |
As you can see from the table, the Leo orbit altitude is significantly higher than other orbits, which is why it is also known as the geostationary orbit. This higher altitude allows the satellite to maintain a stationary position relative to the Earth’s surface, making it an ideal choice for applications that require continuous coverage.
Applications of the Leo Orbit Altitude
The Leo orbit altitude is utilized in various applications, including:
-
Television broadcasting: Satellites in the Leo orbit provide continuous coverage of the entire Earth, making them ideal for global television broadcasting.
-
Weather forecasting: Satellites in this orbit provide real-time data on weather patterns, enabling accurate weather forecasting and early warning systems.
-
Telecommunications: The Leo orbit is used for satellite communication networks, including mobile phone networks, internet connectivity, and corporate communication systems.
-
Navigation: Satellites in the Leo orbit are used for global positioning systems (GPS), providing accurate location and time information.
Challenges and Limitations of the Leo Orbit Altitude
While the Leo orbit altitude offers numerous advantages, it also presents some challenges and limitations:
-
High cost: Launching a satellite into the Leo orbit is expensive due to the increased fuel requirements and the need for powerful rockets.
-
Space debris: The Leo orbit is crowded with numerous satellites, increasing the risk of collisions and space debris.




